Key takeaways
- Altered microbial signature and immune dysfunction may contribute to allergic diseases in infants.1,2
- Prebiotics modulate the composition of gut microbiota and have immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory properties.3
- Evidence suggests that prebiotics can prevent allergic diseases by promoting galectin 9 expression, inducing anti-inflammatory cytokines, and beneficial antibody profile.1-3
Allergy is linked with the disruption of host defense and immune tolerance in children.1,2Numerous clinical findings highlight the beneficial effect of prebiotics (galactooligosaccharide and fructooligosaccharide, GOS & FOS) on the development of gut microbiota and the immune system in infants.4 This article reviews the mechanism through which prebiotics prevent allergy and the benefits of prebiotics containing feed.
Introduction
Allergic diseases affect more than 30% of the world population, particularly younger children. They are linked with the disruption of three interdependent biological systems involved in host defense and immune tolerance- epithelial barrier, microbiota, and immune system.2 This highlights the need for an effective prevention approach in early life.2 Evidence suggests that prebiotics modulate gut microbiota and immune functions. Its supplementation in infant feed may reduce allergic incidences.1,2
Allergic March and prebiotics
Atopic march or allergic march is defined as the typical sequence of allergic reactions and clinical symptoms that appear early in life.5 The primary atopic disease progresses from eczema to asthma, and then to allergic rhinoconjunctivitis.6 Cow’s milk protein is one among the antigens that trigger the aberrant inflammatory responses in early life.7
Evidence suggests that prebiotics balance the T-helper cells (Th2) bias and improves the intestinal processing of antigens in the diet to reduce inflammation and IgE production.8 It was also found that prebiotic mixture GOS/FOS is safe to restrain the atopic march.1
Role of prebiotics in allergy prevention: Mechanism
Numerous clinical studies have shown the role of altered microbial signature and immune tolerance in the pathogenesis of allergy.2,9 Evidence suggests that the development of allergic symptoms might be linked with the early colonization of specific microbiota in the infant’s gut. It has also been reported that the abundance of lactobacilli and bifidobacteria were less in allergic infants as compared to non-allergic infants.4
Prebiotics (GOS/FOS) exert their beneficial effect on the gut microbiota and immune system indirectly by promoting the growth of bifidogenic gut microflora and producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFA). Acetate, butyrate, and propionate are valuable fermentation metabolites with anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory characteristics3(Figure 1).
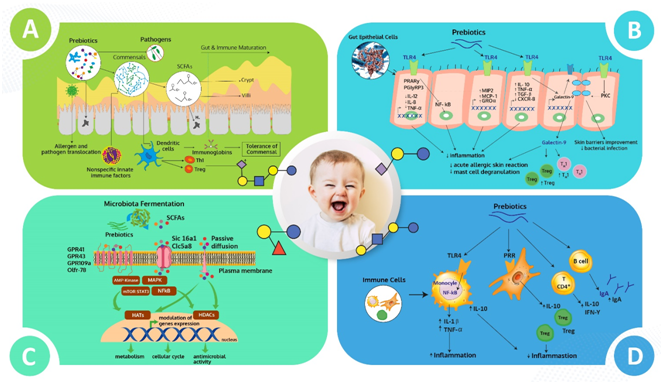
Figure 1: Immunomodulatory effect of prebiotics. A) Promotes growth of beneficial bacteria and immune maturation B) Interacts with gut epithelial receptors to regulates T-cell differentiation, mast cell degranulation, and inhibits inflammation C) Regulates various cellular processes D) Acts directly on immune cells and stimulates the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines.
SCFAs: short-chain fatty acids; Treg: T regulatory cells; Th1: T helper cells; TLR4: toll-like receptor 4; IL: interleukin; TNF: tumor necrosis factor, PPAR-γ: peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PGlyRP3: peptidoglycan recognition protein 3; PKC: Protein kinase C; TGF: tumor growth factor; NF-kB: nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; CXCR: C-X-C chemokine receptor; GRO: growth-related oncogene; MCP: monocyte chemoattractant protein; IgA: immunoglobulin A; IFN-γ: interferon-gamma; AMP-K: AMP-activated protein kinase; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; STAT3: signal transducer and activator of transcription 3; MAPKs: mitogen-activated protein kinases; HDAC: histone deacetylases; HAT: histone acetyltransferases; GPR: G-protein coupled receptor; Slc16a1 and clc5a8:solute carrier family 16 members 1 and 5a8; Olfr-78: olfactory receptor. (Adapted from Brosseau et al., 2019 and Mckeen et al., 2019) 2,10
Possible mechanisms by which prebiotics prevent allergy are as follows:
- Prebiotics modulate the composition of intestinal microbiota by favoring the growth of the beneficial bacteria while limiting pathogenic bacterial growth. Beneficial bacteria produce metabolites such as SCFA on the fermentation of non-digestible dietary fiber. 3-4
- Different cells interact with SCFA such as intestinal epithelial cells (IEC) or innate and adaptive immune cells to regulate various cellular processes such as proliferation, differentiation, etc.2
- The receptor on immune cells interacts with SCFA in gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT), thereby increases immune system reactivity and stimulates the production of interferon-gamma (IFN-γ) and interleukin 10 (IL-10). 3
- Evidence suggests that prebiotics (GOS/FOS) reduces the level of immunoglobulin such as kappa and lambda in the plasma of allergic infants.3
- GOS/FOS also demonstrated an increased level of serum galectin-9 that regulates T-cell differentiation and mast cell degranulation, thereby decreased acute allergic skin reactions.3
Benefits of prebiotic containing infant feed
Infant feed supplemented with prebiotics has the following benefits:1-2,11
- Reduces incidences of recurrent wheezing and atopic dermatitis
- Reduces allergic reaction to food products
- Reduces incidences of allergic urticaria
- Induces beneficial antibody profile
- Halts the atopic march
Numerous clinical studies have supported the role of prebiotics in preventing allergic reactions later in life; some of which are summarized below:
| Prebiotic | Target group, study duration | Study group | Main outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| GOS/FOS (8g/L)1 | Term infants at risk of atopy due to family history 0-6 months | Prebiotic (n=41) Placebo (n=43) | Reduced levels of total IgE, IgG1, IgG2, IgG3 (p<0.01) Reduced levels of cow milk protein-specific IgG1 (p<0.05) |
| GOS/FOS (6.8g/L)9 | Term infants with parental history of allergic disease 0-26 weeks | Prebiotic (n=51) Placebo (n=57) Breastfeed (n=30) | Comparable to breastfed infants in terms of fecal microbiota composition, pH, and metabolites (p<0.0001) Aberrant microbial development in the infant developed eczema at 18 months. It indicated a potential association between onset of eczema and microbial activity |
| GOS/FOS (8 g/L)11 | Healthy term infants with parental history of atopy 0-6 months | Prebiotic (n=66) Placebo (n=68) | Reduced incidences of atopic dermatitis, wheezing, and allergic urticaria (p<0.05) until 2 years of life |
| GOS/FOS (8 g/L)12 | Healthy term infants with parental history of atopic eczema, allergic rhinitis, or asthma 0-6 months | Prebiotic (n=42) Placebo (n=50) | Reduced incidences of any or persistent allergic manifestations (p<0.01), atopic dermatitis(p<0.05), and rhinoconjuctivitis (p=0.05) until 5 years of life |
Conclusion
Owing to the anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory attributes, prebiotics (GOS/FOS) may reduce incidences of allergy in infants later in life.3,11
References
- van Hoffen E, Ruiter B, Faber J, M'Rabet L, Knol EF, Stahl B, Arslanoglu S, Moro G, Boehm G, Garssen J. A specific mixture of short-chain galacto-oligosaccharides and long-chain fructo-oligosaccharides induces a beneficial immunoglobulin profile in infants at high risk for allergy. Allergy. 2009 Mar;64(3):484-487.
- Brosseau C, Selle A, Palmer DJ, Prescott SL, Barbarot S, Bodinier M. Prebiotics: Mechanisms and Preventive Effects in Allergy. Nutrients. 2019 Aug;11(8):1841.
- Ozdemir O. Prebiotics and probiotics in allergy: Potential mechanisms of prebiotics' and probiotics' actions in allergy-(Part 1). MOJ Immunol. 2016 Jan;3(1):00069.
- Boehm G, Moro G. Structural and functional aspects of prebiotics used in infant nutrition. J Nutr. 2008 Sep;138(9):1818S-1828S.
- Wahn U. The Allergic March. World Allergy Organization [Internet] 2015 Sep [Cited 2020 Nov. 17].Available on: https://www.worldallergy.org/education-and-programs/education/allergic-disease-resource-center/professionals/the-allergic-march
- Vandenplas Y, De Greef E, Devreker T. Treatment of Cow's Milk Protein Allergy. Pediatr Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 2014 Mar;17(1):1-5.
- Jo J, Garssen J, Knippels L, Sandalova E. Role of cellular immunity in cow's milk allergy: pathogenesis, tolerance induction, and beyond. Mediators Inflamm. 2014;2014:249784.
- Salazar-Espinosa JF. The atopic march. A literature review. International Journal of Medical Students. 2014 Aug;2(3):119-124.
- Wopereis H, Sim K, Shaw A, Warner JO, Knol J, Kroll JS. Intestinal microbiota in infants at high risk for allergy: Effects of prebiotics and role in eczema development. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2018 Apr;141(4):1334-1342.e5.
- McKeen S, Young W, Mullaney J, Fraser K, McNabb WC, Roy NC. Infant Complementary Feeding of Prebiotics for the Microbiome and Immunity. Nutrients. 2019 Feb ;11(2):364.
- Arslanoglu S, Moro GE, Schmitt J, Tandoi L, Rizzardi S, Boehm G. Early dietary intervention with a mixture of prebiotic oligosaccharides reduces the incidence of allergic manifestations and infections during the first two years of life. J Nutr. 2008 Jun;138(6):1091-1095.
- Arslanoglu S, Moro GE, Boehm G, Wienz F, Stahl B, Bertino E. Early Neutral Prebiotic Oligosaccharide Supplentation reduces the incidence of some allergic manifestations in the first 5 years of life. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2012 Jul;26:49-59.
CVM code: 1610086372523
How did you find the article? Vote Now
AWESOME
GOOD
OK
NOT SO GOOD
FAIL
Recent Articles
Navigating Infant Milk Allergy with the Indian Milk Ladder

By- Danone Nutricia Academy
Danone Nutricia Academy
Cow’s milk protein allergy (CMPA) is a common condition in infants, often appearing within the fi...
Management of Cow Milk Allergy in Infants

By- Danone Nutricia Academy
Danone Nutricia Academy
Cow's milk allergy (CMA) in infants is a common food allergy that can be either IgE or non-IgE medi...
Why hypoallergenic feed is beneficial for infants with CMPA

Amongst the most common food allergies, CMPA is seen to affect children below 1 year of age. It oft...





