AAF may be preferable for infants with multiple food allergies, especially to maintain normal growth
Background
To determine the nutritional adequacy, and growth-promoting efficacy of protein hydrolysate or amino acid-derived formulas (AAF) in infants with Cow’s milk allergy.
Methods
Extensively hydrolyzed whey formula (We) was compared with an AAF in a randomized, prospective follow-up study for 9 months.
We group: n= 22 infants (mean age of 6 months)
AAF group: n= 23 infants (mean age of 7)
Nutritional adequacy and growth were determined.
Results
Both formulas were clinically and biochemically tolerated.
- Mean plasma essential amino acids concentration was lower in We fed group but higher in the AAF fed group compared to values for breast- fed control infants (p=0.00I).
- There was a different trend between the groups in weight – initially weight increased similarly in both groups but later declined in the We fed group while it continued to increase in the AAF group (p=0.09).
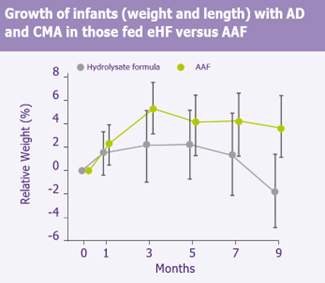
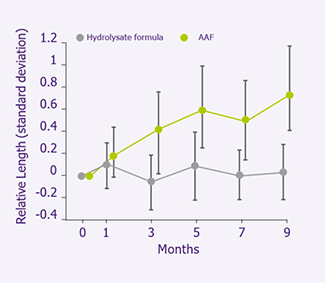
- Length increased in the AAF group but not in the We fed group when compared to the starting length (p=0.006) (see figures).
- Energy intakes were similar between the two groups at 12 months. Energy, protein, and fat intakes from the different formula were relatively similar.
- In both groups, atopic eczema improved significantly (p=0.001) and progressively, with a downward trend in serum total and milk specific IgE concentrations, proving the efficacy of both formulas.
Conclusion
Extensively hydrolyzed formulas are safe and effective for most infants; an amino acid-derived formula may be preferable for infants with multiple food allergies, especially for the maintenance of normal growth
Reference
Isolauri E, Sutas Y, Mäkinen-Kiljunen S et al. Efficacy and safety of hydrolyzed cow milk and amino acid-derived formulas in infants with cow milk allergy. J Pediatr 1995; 127:550-557

